| Previous year question papers |
| 2020 Social science previous year question paper | |
| 2020 Science previous year question papers | | | | | | |
| 2020 math standard Previous year paper | |
| 2020 math Basic Previous year paper | |
| 2020 English previous year paper | |
| 2020 Hindi course A - Previous year paper | |
| 2020 Hindi course B - Previous year paper | |
| 2020 computer previous year paper | |
Secondary School Examination-2020
Marking Scheme – SCIENCE
(SUBJECT CODE: 086) (PAPER CODE : 31/1/2 )
General Instructions: -
1. You are aware that evaluation is the most important process in the actual and correct assessment of the candidates. A small mistake in evaluation may lead to serious problems which may affect the future of the candidates, education system and teaching profession. To avoid mistakes, it is requested that before starting evaluation, you must read and understand the spot evaluation guidelines carefully.Evaluation is a 10-12 days mission for all of us. Hence, it is necessary that you put in your best effortsin this process.
2. Evaluation is to be done as per instructions provided in the Marking Scheme. It should not be done according to one’s own interpretation or any other consideration. Marking Scheme should be strictly adhered to and religiously followed. However, while evaluating, answers which are based on latest information or knowledge and/or are innovative, they may be assessed for their correctness otherwise and marks be awarded to them. In class-X, while evaluating two competency based questions, please try to understand given answer and even if reply is not from marking scheme but correct competency is enumerated by the candidate, marks should be awarded.
3. The Head-Examiner must go through the first five answer books evaluated by each evaluator on the first day, to ensure that evaluation has been carried out as per the instructions given in the Marking Scheme. The remaining answer books meant for evaluation shall be given only after ensuring that there is no significant variation in the marking of individual evaluators.
4. Evaluators will mark( √ ) wherever answer is correct. For wrong answer ‘X”be marked. Evaluators will not put right kind of mark while evaluating which gives an impression that answer is correct and no marks are awarded. This is most common mistake which evaluators are committing.
5. If a question has parts, please award marks on the right-hand side for each part. Marks awarded for different parts of the question should then be totaled up and written in the left hand margin and encircled. This may be followed strictly.
6. If a question does not have any parts, marks must be awarded in the left-hand margin and encircled. This may also be followed strictly.
7. If a student has attempted an extra question, answer of the question deserving more marks should be retained and the other answer scored out.
8. No marks to be deducted for the cumulative effect of an error. It should be penalized only once.
9. A full scale of marks 0-80 has to be used. Please do not hesitate to award full marks if the answer deserves it.
10. Every examiner has to necessarily do evaluation work for full working hours i.e. 8 hours every day and evaluate 20 answer books per day in main subjects and 25 answer books per day in other subjects (Details are given in Spot Guidelines).
11. Ensure that you do not make the following common types of errors committed by the Examiner in the past:-
• Leaving answer or part thereof unassessed in an answer book.
• Giving more marks for an answer than assigned to it.
• Wrong totaling of marks awarded on a reply.
31/1/2 Page 1 of 10
• Wrong transfer of marks from the inside pages of the answer book to the title page. • Wrong question wise totaling on the title page.
• Wrong totaling of marks of the two columns on the title page.
• Wrong grand total.
• Marks in words and figures not tallying.
• Wrong transfer of marks from the answer book to online award list.
• Answers marked as correct, but marks not awarded. (Ensure that the right tick mark is correctly and clearly indicated. It should merely be a line. Same is with the X for incorrect answer.)
• Half or a part of answer marked correct and the rest as wrong, but no marks awarded.
12. While evaluating the answer books if the answer is found to be totally incorrect, it should be marked as cross (X) and awarded zero (0)Marks.
13. Any unassessed portion, non-carrying over of marks to the title page, or totaling error detected by the candidate shall damage the prestige of all the personnel engaged in the evaluation work as also of the Board. Hence, in order to uphold the prestige of all concerned, it is again reiterated that the instructions be followed meticulously and judiciously.
14. The Examiners should acquaint themselves with the guidelines given in the Guidelines for spot Evaluation before starting the actual evaluation.
15. Every Examiner shall also ensure that all the answers are evaluated, marks carried over to the title page, correctly totaled and written in figures and words.
16. The Board permits candidates to obtain photocopy of the Answer Book on request in an RTI application and also separately as a part of the re-evaluation process on payment of the processing charges.
MARKING SCHEME – CLASS X SCIENCE (2019-20) |
QUESTION PAPER CODE: SET 31/1/2 |
S.NO | VALUE POINTS/EXPECTED ANSWER | MARKS | TOTAL MARKS |
| SECTION A |
|
|
1. | O 11 Ketone / - C - | 1 | 1 |
2 | Electromagnetic Induction | 1 | 1 |
3. | a) Thick hair growth in armpits, genital area/thinner hair on arms, legs, face/ more active oil secretion from glands on skin/Occurrence of pimples (any two) b) Imbalance in male – female ratio/ decline in child sex ratio c) Oral pills d) Rate of birth and death | ½ + ½ 1 1 1 | 4 |
4. | a) Human beings are at the top level in any food chain b) Washing of vegetables, fruits, grains thoroughly/Organic farming/ Use of bio pesticides (any one) c) (b) / Trophic level d) (a) / Consumer | 1 1 1 1 | 4 |
5. | (b)- (Fe3O4) OR (b) – Calcium | 1 | 1 |
6. | (d) / All reflecting surfaces OR (d) / Virtual and erect | 1 | 1 |
7 | (d) / Increases heavily OR (d) / 1A | 1 | 1 |
8 | (c) / CaSO4.1/2H2O | 1 | 1 |
9 | (d) / (B), (C) and (D) | 1 | 1 |
10 | (c)/ Sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid [Note: If a candidate writes ‘none of the options is correct’/ ‘sodium hydrogen carbonate’ give full credit.] | 1 | 1 |
11 | (b)/ Chemical energy. | 1 | 1 |
12 | (d)/ Support life | 1 | 1 |
13 | (c) / A is true but R is false | 1 | 1 |
14 | (a) / Both (A) and (R) are true and ( R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A). | 1 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| SECTION B |
|
|
15 | • Oxidation of iron when exposed to air and moisture and acquiring a coating of brown flaky substance. Activity – • Take three test tubes marked A,B and C with clean iron nails in each. • Pour some water in test tube ‘A’ and cork it. • Pour some boiled distilled water and a drop of oil in test tube B and cork it. • Put some anhydrous calcium chloride in test tube ‘C’ and cork it. It will absorb moisture from air leave the test tubes for a few days. • Rusting will take place only in test tube A, which has air and moisture present. 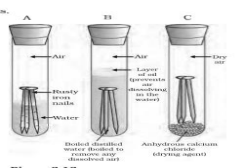 | 1 1 1 | 3 |
16 | • Homologous structures are those which have similar basic structure and origin but modified to perform different functions. • Example: forelimbs of reptiles, amphibians, humans, wings of birds (or any other example) • Yes Similarity in basic design of the structure indicates that their ancestors were common. | 1 ½ ½ 1 | 3 |
17 | Because of scattering of light. Instances: • When a fine beam of light enters a smoke-filled dark room through a small hole. • When sunlight passes through a canopy of dense forest in foggy/ misty conditions. • Blue colour of sky. • Red colour of the sun during sunrise or sunset. (or any other) OR • Prism has 2 inclined refracting surfaces whereas glass slab has 2 parallel refracting surfaces. i) When monochromatic light passes through a glass slab it gets | 1 ½ × 4 1 ½ |
|
| displaced laterally whereas in a prism it gets angularly displaced. ii) When white light passes through a glass slab, it gets laterally displaced whereas in a prism, dispersion takes place. | ½ ½ ½ | 3 |
18 | 
Diagram Labelling | 1 ½ × 4 | 3 |
19 | a) BINARY FISSION MULTIPLE FISSION The parent body divides Parent body show several nuclear division producing many daughter into two identical daughter cells. cells. Occurs only in favourable Occurs in favourable/unfavourble conditions conditions. (or any other) b) A mature spirogyra breaks into smaller pieces and each fragment develops into a new organism | 1 1 1 | 3 |
20 | Products: Hydrogen, Chlorine, Sodium hydroxide Uses: Hydrogen: In the production of margarine/ ammonia/as a fuel Chlorine: Water treatment/ swimming pools/ production of PVC/ Disinfectants/CFCs/Pesticides. Sodium hydroxide: For degreasing metal surfaces/ in making soaps and detergents/ paper making/ artificial fibres. (any one use of these or any other) OR • By recrystallisation of sodium carbonate • Na2CO3 + 10H2O Na2CO3.10H2O • Basic Salt • Permanent hardness | 1 ½ ½ × 3 1 1 ½ ½ | 3 |
21 | i) By dissolving 5g of KMnO4 in 100mL of water/ By dissolving 5g of KMnO4 in water to make a final volume of 100 | 1 |
|
| mL. ii) As an oxidizing agent Purple colour persists Alkaline KMnO4 iii) CH3CH2OH CH3COOH heat | ½ ½ 1 | 3 |
22 | • The adrenaline hormone is secreted into the blood. • The heart beats faster resulting in supply of more oxygen to the muscles. • Blood is diverted to skeletal muscles. • The breathing rate increases. • The blood supply to digestive systems and skin is reduced. OR • Electrical impulses have limited excess to only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue/ neurons, whereas chemical signals can reach each and every cell of the body . Cells need time to reset in order to create repeated/ new electrical impulses whereas no such time is required in chemical communication. | 1 ½ ½ ½ ½ 1 ½ 1 ½ | 3 |
23 | a) V α I or V/I= constant or V = 1R (any of these) 
b) given I = 0.35 A, V = 1.4 V R = V/I = 1.4 0.35 = 4.Ὠ | 1 1 1 | 3 |
24 | i) H = I2Rt ii) H = V.I.t = V.Q Given : V = 40 volts , Q = 96000 C H = 40 V × 96000 C = 3.84 × 106J | 1 ½ 1 ½ | 3 |
| SECTION C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 | a) • The highly exothermic displacement reaction between iron oxide and aluminum powder. • It is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts. • Fe2O3(s)+ 2 Al(s) → Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat b) It is placed above iron / towards top in the reactivity series. c) Oxidized → Al. Reduced → Fe2O3 | 1 1 1 1 ½ ½ | 5 |
26 | a) A current carrying solenoid is called an electromagnet /when soft iron is placed inside a solenoid carrying current, the soft iron piece behaves like a magnet so long as electric current passes through it. The magnet so formed is electromagnet. Uses: In electric motors, electric bells, ( or any other ) b)  (Direction of current) c) Soft iron core is used to increase the strength/power of the electro magnet. (Direction of current) c) Soft iron core is used to increase the strength/power of the electro magnet. d) i) By increasing the current ii) By increasing the number of turns in the coil. | 1 ½ + ½ 1 ½ ½ ½ + ½ | 5 |
27 | i) 
ii) iii)   | 1 1 |
|
| 
In case (i) sign is positive and m> 1 (ii) sign is positive and m < 1 OR Given h = + 4.0 cm, u = -25.0 cm, f = -15.0 cm i) image distance v = ? ; mirror formula :1/u +1/v= 1/r Or 1/v =1/r-1/u; = -1/15– (-1/25) = 1/15 + 1/25 = -5+3/75
v = - 37.5 cm The screen should be placed 37.5 cm in front of the mirror. ii) m = ℎ1 /h = -u/v : ℎ1 = -u/v. h = -37.4 x 4/-25 ℎ1 = - 6.0 cm (size of the image). iii)  Note: Deduct half mark for not showing arrows in ray diagrams. Note: Deduct half mark for not showing arrows in ray diagrams. | 1 ½ + ½ ½ + ½ ½ ½ 1 ½ ½ ½ ½ 1 | 5 |
28 | a).Study of heredity and variations in organisms b). • Gene – A segment of DNA which is a carrier of genetic information from one generation to another. • Genes are located on the chromosomes. c). (i) Natural selection – selection of the fittest organisms which are then transferred over generations leading to the evolution of a new species. (ii) Genetic drift – It is the random change in the frequency of genes in a small population over successive generations. (iii) Reproductive isolation–when some members of a particular species are not able to mate with other members of the same species due to geographical/environmental barriers leading to origin of a new species. (any other factor) | 1 ½ ½ ½ + ½ ½ + ½ ½ + ½ | 5 |
29 | i) E, it has 4 valence electrons. ii) B, it needs only 2 electrons to attain stable configuration. iii) D , it loses two electrons to attain stable configuration . iv) F, it has the largest size since size increases down the group. v) Noble gases, outermost shell is complete. OR • Atomic size is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom . • Picometer /pm • Trends in atomic radius In a group: increases down the group ; due to addition of a new shell . In a period: decreases from left to right ; due to increase in pulling power of nucleus/ addition of electrons in the same shell. | ½ + ½ ½ + ½ ½ + ½ ½ + ½ ½ + ½ 1 1 ½ 1 ½ 1 | 5 |
30 | a) Rate of breathing is faster in aquatic organisms because the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is lower as compared to the amount of oxygen in air. b)  | ½ 1 |
|
| Diagram 5 labellings OR a) A pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. b) A kidney has a large number of filtration units called nephrons. Each nephron has a bunch of capillaries called glomerulus. Blood containing nitrogenous waste gets filtered in the glomerulus. Filtrate gets collected in Bowman’s capsule. Some substances such as glucose amino acids, salts and water are selectively reabsorbed as urine flows through nephron tube.The urine formed in each kidney is eventually stored in the urinary bladder | 1 ½ x 5 ½ x 4 ½ ½ ½ ½ ½ ½ | 5 |










0 Comments