Most important question for class 10 science
2.What is Double fertilization?
Aerobic respiration: is a fixed metabolic reaction that takes place in the presence of oxygen, going on in a cellular to transform chemical energy into ATPs.
Anaerobic respiration: is a process of cellular respiration in which the excessive energy electron acceptor is neither oxygen nor pyruvate derivatives.
Three different methods of contraception:
Barrier method:
1.Physical devices like condoms, diaphragm and cervical caps are used. They prevent entry of sperm in female genital tract, so, act as a barrier between them.
2.Other contraceptive devices are loop or copper-T, are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy.
2.HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, attacks the immune system, which is your natural defense against illness.
9.(A). Explain the terms: (I)implantation (II) Placenta
(B). What is the average duration of Human pregnancy?
Answer:
(i) Implantation of Zygote: Embryo moves down in uterus and settles there in its wall. This attachment is called Implantation of Embryo.(ii) Placenta: Embryo gets nutrition from mothers blood by help of a special tissue called placenta.
2.The average duration of of human pregnancy in human females or gestation period in human females is 280 days or 40 weeks.
10.List any four reasons for vegetative propagation being practiced in the growth of some type of plants.
(i) The plants grown by vegetative propagation usually needs less attention in their early years than the plants grown from seeds.
(ii)The plants are genetically similar.
(iii)It helps in producing those plants which either produce very few seeds or produce such seeds which are not viable.
(iv) It can be used to produce plants that reach maturity and produce fruits and seeds faster.
11.Describe in brief the role of
(I) Tests (II) seminal vesicle
(III) Vas Deferens
(IV) Ureter and
(V) Prostate gland in human male reproductive system.
Testis: Testes are oval shaped primary reproductive organs in men. The function of testes is to produce sperms and male sex hormone testosterone. The scrotum provides optimal temperature for the formation of sperms.
Seminal vesicle: Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin walled muscular elongated sac which secrete fluid for nourishment of sperms.
vas deferens: The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens to organs called seminal vesicles where the sperms get nourishment and stored.
Ureter: It is the tube that carries urine from kidney to the urinary bladder.In humans there are two ureters one attached to each kidney.
Prostate glands: Prostate glands produce a fluid which is released in the urethra along with secretion of seminal vesicles for nourishment and transportation of sperms.
12.Draw a diagram of a human female reproductive system and label the part
Answer:
(I) The Human female reproductive system which produces eggs is Ovary
(II) The human female reproductive system where fusion of egg and sperm takes place is Fallopian tube.
(III) The human female reproductive system where zygote is implanted is Uterus.
The diagram is as follows:
If the egg is not fertilized, then the thick and soft inner lining along with the dead egg and blood vessels, of uterus gets out of vagina in bleeding form. This process is known as Menstruation. It occurs when sperms are not available in female body
13.”The sex of the children is determined by what they inherit from their father and not their mother”.Justify
(a) "The sex of the children is determined by what they inherit from their father and not their mother. This statement is completely justified and can be proved as follows: A male has XY chromosomes and a female has XX chromosomes.
1. If a sperm carrying X chromosome from male gets combined with the X chromosome from female, then the combination will be XX and child will be a baby girl.
.
2. If a sperm carrying Y chromosome from male gets combined with the X chromosome from female, then the combination will be XY, and the child will be a baby boy.
14.Distinguish between Acquired and inherited traits by giving one example of each ? Why are Traits Acquired during the lifetime of an individual not inherited?
Answer
The changes in germ cells of the reproductive tissue of a sexually reproducing organism, which can be passed on to the next generation are called inherited traits. For example colour of the eye.
The changes in non-reproductive tissue of an organism, which cannot be passed on to the progeny, because they do not involve any change in the DNA of germ cells, are called acquired traits. For example reduction in weight due to starvation.
These are the traits acquired during the lifetime of an individual and are not inherited because of lack of change in germ cells that participate in the reproduction process.
15. A Blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is cross bred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
(A). State the colour of flower you would expect in their F₁ Generation plants.
(B). What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F₂ Generation if flowers of F₁ plants are self- Pollinated?
(C). State the expected ration of the genotypes BB and bb in the F₂ progeny.
(a) In the first generation i.e. in F, generation, all the flower plants will be of blue color. It can be shown as follows:
(b) When flowers of f1 generation are self pollinated:
So, in F2 generation, there will be three blue Flowers and one white flower. So they ratio of blue flower plant to ratio of white flower plant is 3:1 But we need to find the ration percentage of white flower which is calculated as follows:
So, Ratio percentage of white flower plant is 25% (c) The expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny is as follows:
16. Explain chlor-Alkali process
When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. This process is called the chlor-alkali process.
2NaCl(aq) + 2H₂O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl₂(g) + H₂(g)
Sodium chloride Sodium hydroxide Chlorine gas
Uses of NaOH obtained from chlor-alkali process:
(i) It is used for de-greasing metals, soaps and detergents.
(ii) It is used for making paper and artificial fibers.
17.Give reason to justify that Aluminium Oxide is an Amphoteric Oxide.Also give another example of Amphoteric Oxide.
Answer:
Aluminium oxide reacts with both acidic and basic substances to give neutralization reaction and hence cannot be called a true acid as well as base. Hence it is called amphoteric oxide.
Al₂O₃+6HCl→2AlCl₃+3H₂O>> Neutralisation Reaction with hydrochloric acid ( behaves like a base )
Al₂O₃+2NaOH→2NaAlO₂+H₂O>> Neutralisation reaction with Sodium hydroxide ( behave like an acid )
(b) lonic compounds are bound to each other with strong attraction force. Hence they are in solid form and their ions are not mobile. When in molten state the ions become mobile and act as carriers for charge and hence conduct electricity.
18.The Reaction of metal (X) with ferric oxide is highly exothermic metal(X) is obtained from its oxide by electrolytic reduction. Identify (X) and write its reaction with Ferric Oxide.
Answer
The reaction of metal X with ferric oxide is highly exothermic and also metal X is obtained from its oxides by electrolytic reduction.
So metal X is Aluminium and its reaction with ferric oxide is:
2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) ; H = - 850 kJ
19. With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compound are formed.State any three general properties of ionic compounds.
Ans.
Ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.These compounds are composed of one part of metal and other part of non-metal, e.g. sodium oxide Na20.


Properties of ionic compounds
These compounds are water soluble.
These compounds have high melting and boiling points.
These compounds conduct electricity in molten form or in the form of aqueous solution.
20.Explain in detail – Reaction of metals with water.
Answer
Reactions of metals with water
When a metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and hydrogen are formed.
For example:
Sodium reacts vigorously with water.
sodium + water ➞ sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ➞ 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Calcium reacts readily with water.
calcium + water ➞ calcium hydroxide + hydrogen
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) ➞ Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Calcium hydroxide is slightly soluble in water so once the solution is saturated, it starts to become milky as solid calcium hydroxide appear.
The apparatus below is used to react calcium with water and collect the gas. This would not be used with sodium or potassium as they float and the reaction is too vigorous.
21.Explain in detail – Reaction of metals with Acids.
2.What happens if it is Nitric Acid?
Answer:
Most metals react with acids in a single replacement reaction in which the metal replaces the hydrogen ions in the acid.
Mg + 2 HCl ➡️H₂ + MgCl₂
A few metals that don't do this are the coinage metals (Cu, Ag, Au). These metals tend to only react with concentrated nitric acid in an oxidation-reduction reaction where the metal gets oxidized and some of the nitrate gets reduced to nitrogen dioxide.
Cu + 4 HNO₃ ➡️ Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2 NO₂ + 2 H₂O
This reaction would be a bit different for Ag going to Ag+ ion or Au going to the Au3+ ion.
2.Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2). But magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) react with very dilute HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
22.Give 2 uses of Baking soda, HCL, Chlorine Gas, Bleaching powder, POP, washing soda.
Answer:
1.uses of Baking Soda
- Treat heartburn. Heartburn is also known as acid reflux.
- Mouthwash. Mouthwash is a great addition to a good oral hygiene routine
- It is used for bleaching dirty clothes in the laundry, as a bleaching agent for cotton and linen in the textile industry.
- It is a strong oxidizing agent, hence used as an oxidizer in many industries.
- It is used as a disinfectant which is used for disinfecting water to make potable water.
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
- It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
- Plastering fractured bones
- Making toys
- Decorative materials
- It's used industrially to process steel
- The material of choice for suspension bridges and cars and trucks.
- Hydrochloric acid is also used in the production of batteries, photoflash bulbs and fireworks.
- It's even used to process sugar and make gelatin.
- It is used to treat drinking water and swimming pool water.
- It is also used to make hundreds of consumer products from paper to paints, and from textiles to insecticides.
- About 20% of chlorine produced is used to make PVC.
23.What is water of crystallization? Name and formulate any 2 examples?
Answer
Water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. Or we can say water stoichiometrically bound into crystal.
For example, chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate is CuSO4 · 5H2O. Copper sulphate has 5 molecules of water of crystallisation.
sugar molecules within the honey begin to form crystals, through the process of crystallization.
24.What is tooth Enamel chemically? State the condition when it starts corroding?
Answer:
White tooth enamel is calcium phosphate which is very hard. It gets affected when the pH of our mouth falls below 5.5.
The bacteria present in our mouth breaks down the food particles into acids which damage our teeth by corroding them.
What happens when food particles left in the mouth after eating degrade?
Answer:
The bacteria present in our mouth breaks down the food particles into acids which damage our teeth by corroding them.
Why do doctors suggest use of tooth powder/toothpaste to prevent tooth decay?
Answer:
Toothpaste can slow down the rate of tooth decay. Toothpastes clean teeth and increase their strength. During decay, teeth wear away, become discolored and may become sensitive.
25. Give preparation Reaction of : Baking soda,Bleaching powder, Pop
Answer:
Preparation of Baking Soda
It is prepared by reaction of cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride with ammonia and carbon dioxide. "Bleaching powder" is made by the action of chloride gas on calcium hydroxide, the reaction being essentially:
2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → Ca(OCl)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O.
Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum at 373 K. On heating, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate semi hydrate (CaSO4.1/2 H2O) which is called Plaster of Paris.
Plaster of Paris is used in hospitals for setting fractured bones in the right position to ensure correct healing.
26.Explain double decomposition reaction with an example?
Answer:
A double decomposition reaction is a type of decomposition reaction in which two constituent reactants interchange positive and negative ions and form two new compounds.
Example. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + HOH(l)
27.What is meant by spectrum of white light? How can we recombine the components of white light after a prism has separated them ?Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
Answer: The coloured pattern VIBGYOR formed by a prism by splitting the incident white light is called a spectrum. By having two prisms, inverted to each other, one can recombine the light to get white light again.
28.Explain why do the planets not twinkle but the star twinkle .
Answer:
Light of the star is bent many times and in random directions as light is bent when it hits a change in density. This random refraction results in the star winking out - twinkling.Planets are closer to Earth and so appear as tiny disks in our sky.
The light from these little disks is also refracted by Earth’s atmosphere, as it travels toward our eyes. Due to the planets’ apparent closeness to Earth, the light coming from these celestial bodies does not bend much due to Earth’s atmosphere. Also being not a point source but appearing as disks, they comprise of several point sources- lights of which are coming at the same time.
So a deviation in light path of one point source can cancel with deviations of other and would average out to give rise to a steady shine. Therefore, the light coming from our solar system’s planets does not appear to twinkle like stars.
29.Light of Red colour are used for danger signals .— Give reason
Answer:
Danger signals are red in color because it is scattered the least by air molecules. The effect of scattering is inversely related to the fourth power of the wavelength of a color. Since the color red has the highest wavelength of all the colors we can see it scattered the least. So, red light is used as a danger signal as it is able to travel the longest distance through the fog, rain, etc.
30.What is the colour of the clear sky during day time?Give reason for it?
Answer:
The colour of clear sky is blue during the day time. The sky appears blue because of scattering of light by our atmosphere. Among the different colours of white light, the blue colour gets scattered the maximum due to shorter wavelength than red.
31.A concave lens has focal length of 20cm. At what distance from the lens 5 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at 15cm from the lens ? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
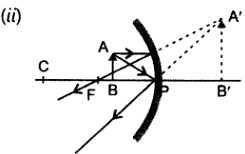
32.Draw the ray diagram in each case to show the position and nature of image formed when the object is placed.
(i)At the center of curvature of a concave mirror.
(ii)Between the pole p and focus F of A concave mirror
(iii)In-front of a convex mirror
(iv)At 2F of a convex lens
(v)In-front of concave Lens
Answer: Nature of image: Real, inverted and same size image is formed at the centre of curvature. Nature of image: Virtual, enlarged and erect image is formed behind the mirror Nature of image: Virtual, erect and diminished, image is formed behind the mirror. Nature of image: Real, inverted and size to size, image is formed at 2F on the other side of lens. Nature of image: Virtual, erect and diminished image is formed between O and F on the same side of object.
33.Draw the given diagram and show the path of the refracted ray
34.An object 2cm in size is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15cm at what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? What will be the nature and the size of the image formed? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
Answer:
So, screen should be placed at a distance of 30 cm on the same side of the object in order to obtain a sharp image.
Since, |v| = |u| = 2f, it means that the object is placed at the centre of curvature (c) of a concave mirror, the image formed is at the centre of curvature,real and inverted and of the same size as the object.
35.Distinguish between a real and a virtual image of an object what type of image is formed (i) By a plane mirror, (ii) On a cinema screen?
Answer:
If light rays after reflection converge to a point to form an image on its own, it is called a real image. If they are diverging, then they form a virtual image. Real image can be obtained on a screen, while a virtual image cannot be.
(i) Plane mirror forms virtual image.
(ii) On cinema screen, real image is formed.
36.Define ‘Refractive index of a transparent medium ‘. What is its unit ? Which has a higher refractive index, glass or water?
Answer:
The ratio of the speed of light in the free space (c) to the speed of light in given medium (v) is called its refractive index. n = c/v. It has no unit. Glass has more refractive index than water.
37.A convex lens of focal length 25cm and a concave lens of focal length 10cm are placed in close contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of this combination.
Answer:
Power of combination = P1 + P2.
P = 4D – 10D = -6D.
Lens power of the combination is -6D.
Since it is negative therefore the new lens will behave like concave lens having a focal length of 16.6cm.
38.(a) Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
(b) Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
(c) Why does distilled water not conduct electricity whereas rain water does?
Answer:
(a) The acidic behaviour of a substance is due to the presence of H+ ions. As acids dissociate into their ions only in the presence of water, the acidic character of acids cannot be seen in the absence of water.
(b) Acids dissociate to release H+ ions and an anion, when dissolved in water. When electric current is passed through an aqueous solution, the ions start moving toward oppositely charged terminals of the battery, henceforth, conducting electricity.
(c) Distilled water is the purest form of water. The process of distillation makes the water free from all the ionic species, whereas rainwater consists of plenty of impurities. Thus, it contains numerous ions such as H+, CO3-, SO42- etc. Therefore, rainwater conducts electricity.
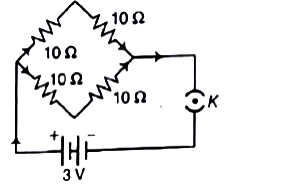
39. Find the current drawn from the battery by network of four resistors shown in the figure?
V = 3V
R₁ = R₂ = R₃ = R₄ = 10Ω Here,
R₁ and R₂ are connected in series
And, R₃ and R₄ are connected in series.
Now, by Ohm’s Law V = I x R
I = VR = 310
∴ I = 0.3A
Thus, Current drawn by the resistor from the battery is 0.3
40.An electric bulb of resistance 200Ω draws a current of 1 Ampere. Calculate the power of the bulb the potential difference at its ends and the energy in kWh consumed burning it for 5h.
Answer
Power of the bulb,
= l²R = (1)² x 200
⇒ P = 200 W
Energy consumed by bulb in 5h in burning
= Power x Time
= 200 x 5 = 1000
1000Wh = 1 kWh
41.Calculate the resistance of 1Km long copper wire of radius 1mm. Resistivity of the copper is 1.72 x 1 0-8) Here, length of the wire?
Answer:
radius of the wire
of cooper,
If R is the resistance of the given wire, then
42.An electric bulb is rated at 60W, 240V calculated its resistance. If the voltage drops to 192V. Calculated the power consumed and the current drawn by the bulb.(Assume that the resistance of the bulb remain unchanged.
Answer:
According to the Fleming's left-hand rule, the charged particle should be a positively charged in order to experience the force in the direction out of the page after interaction with the magnetic field.
43.A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a Galvanometer what will happen if a bat magnet is
(a) Pushed into the coil.
(b).withdrawn from inside the coil.
(c). Held stationary inside the coil?
Answer
When a coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer, following observations will take place for each option:
(I) If a bar magnet is pushed into the coil, an electric current will be induced in coil due to electromagnetic induction.
(ii) If a bar magnet is withdrawn from inside, again current will be induced in the copper wire due to electromagnetic induction but this time the direction of current will be reverse in galvanometer.
(iii) If a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil then no current is induced and therefore there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
44.Explain the working of electric motor.
Answer
Electric motors involve rotating coils of wire which are driven by the magnetic force exerted by a magnetic field on an electric current. They transform electrical energy into mechanical energy.
1.) An electric current in a magnetic field will experience a force
2.) If the current carrying wires are bent into a loop when the two sides of the loop which are at right angles to the magnetic field will experience forces in opposite direction.
3.) The pair of forces creates a turning influence or torque to rotate the coil.
4.) Particle motors have several loops on an armature to provide a more uniform torque.
45.Explain the function of the following parts of an electric motor.
(i) Armature
(ii) Brushes
(iii) Split
Answer
(i) Armature: It is a rectangular iron core wrapped by the copper coil through which electricity passes and due to magnetic field it experiences a force and rotates.
(ii) Brushes: It conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly in a rotating shaft.
(iii) Split Ring: It helps to reverse the direction of current in the circuit.
46.A given length of a wire is doubled on itself and this process is repeated once again. By what factor does the resistance of the wire change?
Answer
If the length of wire is drawn to double its length then length has increased double and area get reduced to helf
So, Resitance will be 4 times.
And, again the process is repeated so resitance will increase 4 times. So tallay, the resitance get increased by 16 times.
47. What do the following circuit symbols represent ?
The potential difference between the terminals of an electric heater is 60 V when it draws a current of 4A from the source. Find the resistance of heater when in use.
Answer
Given :
Potential Difference of heater = 60v
current I=4A
Resistance =R?
By Ohm's law :
V=IR
R=V/R
=60/4=15 ohms
Now if potential is increased to 120 V
I=?
V=I X R
I=V/R
=120/15
=8 A
Hence current drawn by heater is 8A.
48.Two coils of insulated copper wire are wound over a non conducting cylinder as shown . Coil I has larger number of turns
(i). write your observation when,
(a)Key K is closed
(ii). when the current is passed continuously through coil I.
Give reason for your observations
(iii). Name and state the phenomenon responsible for the Above observation?
(iv) Write the name of the rule that is used to determine the direction of current produced in the phenomenon.
(v) Name the two coils used in this experiment?
Answer
(i) (a) When key is closed, the galvanometer needle deflects momentarily in one direction. Reason: When key is closed, magnetic field lines around coil 2 increases momentarily. This causes an induced current to flow through it and hence deflection occurs in one direction.
(b) When key is opened, the galvanometer needle deflects again momentarily but in opposite direction. Reason: When key is open, magnetic field lines around coil 2 decreases momentarily. This causes an induced current to flow in opposite direction. Hence, deflection occurs in opposite direction.
(ii) When current is passed continuously through coil I, no deflection is observed in the galvanometer. Reason: There will be no change in magnetic field lines passing through the coil 2. Hence, no induced current will be set up in coil 2.
(iii) The phenomenon observed in above cases is electromagnetic induction. It is a process by which a changing magnetic field in a conductor induces a current in another conductor placed nearby.
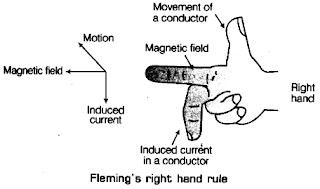
(iv) Fleming’s right hand rule
(v) Coil I – Primary coil Coil II – Secondary coil.
49.State the rule to determine the direction of A
(A). Magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current .
(B). Force Experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it .
Answer
(i) Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb Rule: The- direction of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying conductor is given by Maxwell’s right hand thumb rule.
The thumb rule states that, if the current carrying conductor is held in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of the current, then the direction of the curl of the fingers will given the direction of the magnetic field. This rule can also be stated as if we consider ourselves driving a corkscrew in the direction of the current, then the direction in which we rotate the screw is the direction of the magnetic field.
Maxwell's corkscrew rule
(ii) Fleming’s Left Hand Rule: The direction of force which acts on the current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is given by Fleming’s left hand rule. Fleming’s left hand rule gives us the force experienced by a straight current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to it. The rule states that, stretch the forefinger, the central finger and the thumb of the left hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the central finger in the direction of current, then the thumb points in the direction of force in the conductor.
(iii) Fleming’s right hand rule The direction of induced current in a straight conductor is given by Fleming’s right hand rule. Fleming’s right hand rule gives the direction of induced current in a coil due to it's rotation in a magnetic field. Rule states that if you stretch the thumb, forefinger and the central finger of the right hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the directions of magnetic field, thumb in the direction of motion of the conductor, then the central finger points in the direction of current induced in the conductor.
50.A). Describe an activity to demonstrate the pattern of magnetic field lines around a straight conductor carrying current?
B). State the rule to find the direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor.
C). What is the shape of a current carrying conductor whose magnetic field pattern resembles that of a Bar-Magnet?
Answer
(a) Aim: To study the magnetic field due to a straight current-carrying conductor. Apparatus Required: A thick conducting wire, battery, rheostat, magnetic needle, ammeter (0-5 A), key, a cardboard, a stand to hold the wire, iron filings and sprinkler of iron filings. Procedure: Attach the thick wire through a hole at the middle of the cardboard and clamp it in a stand. Attach the ends of the wire through a key, variable resistor and an ammeter. on either side of a battery and hold it vertically and perpendicularly to the board. Spread the iron filings uniformly on the cardboard and place the magnetic needle on the board. Close the key and tap the cardboard slightly and observe the orientation of iron filings.
Magnetic field around a straight conducting wired concentric circles indicate the field lines Observation: Just on closing the key, the iron filings are aligned in the pattern of concentric circles around the wire. Conclusion: A current-carrying conductor is a source of magnetic field. The magnetic field is in the form of concentric circles whose centre lies on the wire.
(b)Right – Hand thumb Rule: Hold the current-Carrying wire in your right hand, such that the thumb indicates the direction of current, then the folded fingers will indicate the direction of magnetic field (lines) surrounding the wire.















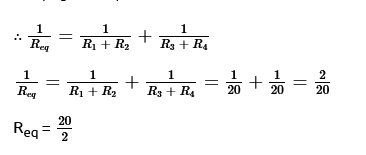
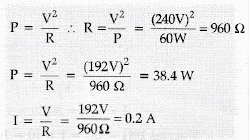

















0 Comments